Aneurysm Clipping: Surgical Treatment for Cerebral Aneurysms

Nearly all patients with brain aneurysms, also known as cerebral aneurysms, can be safely and effectively treated with the latest techniques. Most brain aneurysms can be treated using minimally invasive endovascular techniques, however some patients will require surgery (clipping) to treat their aneurysm. Due to the complexity of brain aneurysms, treatments should be uniquely tailored to each individual. There are several factors that will help determine how and whether to treat an aneurysm.
Treating a brain aneurysm may require a surgical procedure or endovascular treatment. For patients with unruptured aneurysms, it is best to talk to an experienced physician to discuss possible treatment options. At this time, a health care provider will be able to discuss possible risks and recommend treatments.
There are two common surgical treatment options for repairing a ruptured brain aneurysm – surgical clipping and endovascular coiling. Both of these procedures come with potential risks and benefits to patients. The information below may be helpful in learning more about surgical aneurysm clipping.
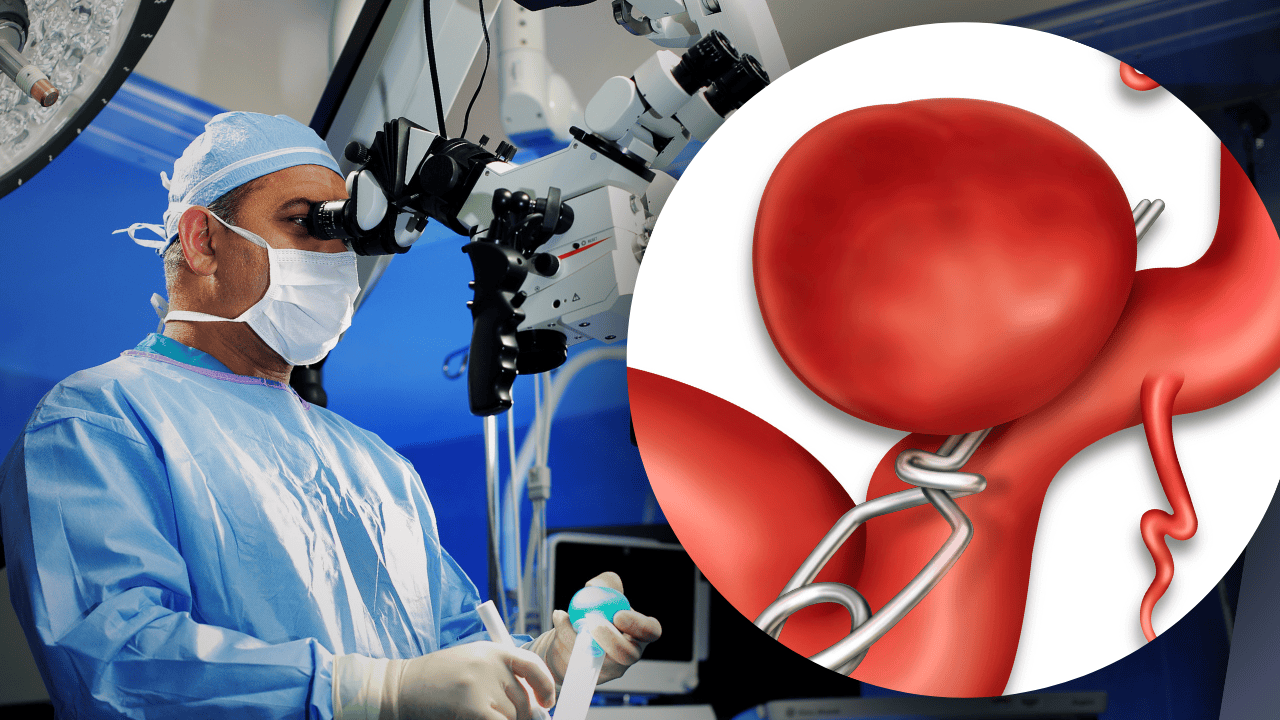
Aneurysm clipping is a procedure where a surgeon uses a metal surgical clip to close off an aneurysm in the brain. The surgeon makes a small opening on the skull to reach the brain, and a microscope is used to perform the detailed procedure. During this time, the surgeon will utilize precision techniques to avoid harming nerves, blood vessels or brain tissue.
The surgical clipping procedure will isolate the aneurysm from the surrounding brain tissue, which will effectively cut off blood flow from the artery to the aneurysm.
Surgical clipping can be very effective. Typically, aneurysms that are clipped will not return. For unruptured aneurysms, the clipping procedure typically will provide an effective treatment option. For ruptured aneurysms, clipping can stop bleeding, while also preventing future bleeding in the brain.
Typical recovery time from aneurysm clipping surgery is approximately 4 to 6 weeks, following a brief hospital stay. However, each patient is unique and individual recovery time should be discussed with a physician. You will likely feel very tired for several weeks following surgery and may also have headaches or trouble concentrating for up to 2 weeks.
For more than 30 years, the experienced physician team at New Jersey Brain and Spine’s neurovascular center has delivered highly-skilled and compassionate care to more than 40,000 patients with complex brain, spine and neurological conditions. Learn more about our neurovascular team, including Dr. Karimi and Dr. Walzman, by watching this video. Please contact us today to decide if we are the right option for your care and treatment.
| “Having a physician who is an expert in all three neurovascular modalities—surgery, embolization and radiosurgery—provides more tailored therapies and improves care quality.” |
We also offer an expert second opinion service should you wish to discuss your treatment options. For more information, or to request a second opinion, reach out to us immediately by calling 201-342-2550 or emailing us at secondopinion@NJBrainSpine.com.