The term vasculitis refers to inflammation causing irritation of the arterial system resulting in narrowing or occlusion of blood vessels. Vasculitis patients present with headaches, alteration of consciousness (encephalopathy), symptoms of stroke or coma. CT and MR are non-specific although findings on cerebral angiography are often diagnostic demonstrating irregular narrowing of blood vessels (stenosis) (Figure 1,2).
An analysis of spinal fluid as obtained from a spinal tap may also be helpful although a brain biopsy is sometimes necessary to facilitate diagnosis. Treatment depends on the underlying cause of vasculitis but usually requires immunosuppressant agents.
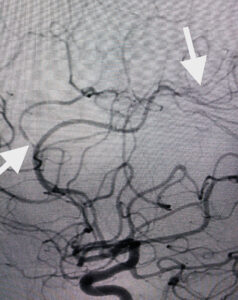
Figure 1
Lateral carotid cerebral angiogram demonstrating areas of focal narrowing (arrows) typical for patients with cerebral vasculitis.